How to Create REST API


Your lightweight Client for API debugging
No Login Required
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!










A REST API (Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interface) is one of the most widely used methods for enabling communication between client applications and servers. It allows developers to expose data and functionality over HTTP in a standardized, scalable, and platform-independent way.
Building a REST API involves designing endpoints, defining request and response formats, implementing CRUD operations, and ensuring proper security and error handling.
Whether you’re creating a simple API for internal use or a production-grade service for public consumption, understanding the fundamentals is essential to deliver reliable and maintainable solutions.
Understanding REST API
A REST API (Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interface) is a type of API that follows the constraints of the REST architectural style, enabling communication between client and server systems over the internet.
It allows different software applications to exchange data efficiently using standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, which correspond to CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) on resources.
The fundamental concept of REST is centered around resources, which are any kind of content or data that the server provides to the client. Each resource is identified by a unique URI (Uniform Resource Identifier), typically represented as a URL.
Clients interact with these resources by sending HTTP requests to specific URIs, and servers respond with representations of the resources, usually in JSON format, though other formats like XML or HTML can be used.
REST API design follows key principles, including:
- Statelessness: Each client request contains all necessary information for the server to fulfill it, with no session state stored on the server.
- Client-Server Architecture: The client and server operate independently, promoting scalability and separation of concerns.
- Cacheability: Responses can be designated as cacheable to improve performance.
- Uniform Interface: A consistent and standardized way to interact with resources, using well-defined HTTP methods and status codes.
- Layered System: The architecture can be composed of multiple layers to enhance scalability and security
Setting Up the Development Environment
To start creating a REST API, a well-prepared development environment is essential. The most popular choice for beginners and seasoned developers alike is Node.js with the Express framework, as it offers simplicity, flexibility, and powerful features for building RESTful APIs.
Here’s how to set up the development environment step-by-step:
1. Install Node.js and npm
Begin by downloading and installing Node.js from its official website. npm (Node Package Manager) comes bundled with Node.js and allows easy installation of libraries and dependencies. Verify their installation with:
node -v
npm -v
2. Create a Project Directory
Choose a location on your computer and create a dedicated folder for your API project:
mkdir my-REST-api
cd my-REST-api
3. Initialize the Node.js Project
Use npm to initialize a new Node.js project. This creates a package.json file that manages project metadata and dependencies:
npm init -y
4. Install Express and Other Dependencies
Express is the core framework for creating routes and managing HTTP requests. Install it along with other useful middleware libraries for handling JSON payloads, security, logging, and cross-origin resource sharing:
npm install express body-parser cors helmet morgan
5. Set Up the Main Application File
Create a file named app.js (or index.js) in the project root. This will be your main server file. Example of a basic Express server setup:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.use(express.json()); // Enable JSON parsing
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Welcome to the API!');
});
const PORT = 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on port ${PORT}`);
});
6. Run and Test Your Server
Start your Node.js server using:
node app.js
Visit http://localhost:3000 in your browser to see the welcome message.
This environment setup lays a strong foundation for building REST APIs using Node.js and Express, combining ease of use with extensibility for complex features as your project grows.
Creating a Simple REST API Step-by-Step
Building a REST API with Node.js and Express can be straightforward by following these steps:
1. Setup Project
Create a new project directory and initialize it with npm to create a package.json file:
text
mkdir REST-api
cd REST-api
npm init -y
2. Install Express
Install Express, the web framework used to build the API server:
text
npm install express
3. Create Main Server File
Create a file named app.js in the project root and set up a basic Express server:
javascript
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.use(express.json()); // Middleware to parse JSON request bodies
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Welcome to the REST API!');
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on http://localhost:${port}`);
});
4. Define RESTful Endpoints
Add routes for common CRUD operations on a resource, for example, users:
javascript
let users = [
{ id: 1, name: 'Alice' },
{ id: 2, name: 'Bob' },
];
app.get('/users', (req, res) => {
res.json(users);
});
app.get('/users/:id', (req, res) => {
const user = users.find(u => u.id === parseInt(req.params.id));
if (!user) return res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' });
res.json(user);
});
app.post('/users', (req, res) => {
const newUser = {
id: users.length + 1,
name: req.body.name
};
users.push(newUser);
res.status(201).json(newUser);
});
app.put('/users/:id', (req, res) => {
const user = users.find(u => u.id === parseInt(req.params.id));
if (!user) return res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' });
user.name = req.body.name;
res.json(user);
});
app.delete('/users/:id', (req, res) => {
const index = users.findIndex(u => u.id === parseInt(req.params.id));
if (index === -1) return res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' });
const deletedUser = users.splice(index, 1);
res.json(deletedUser[0]);
});
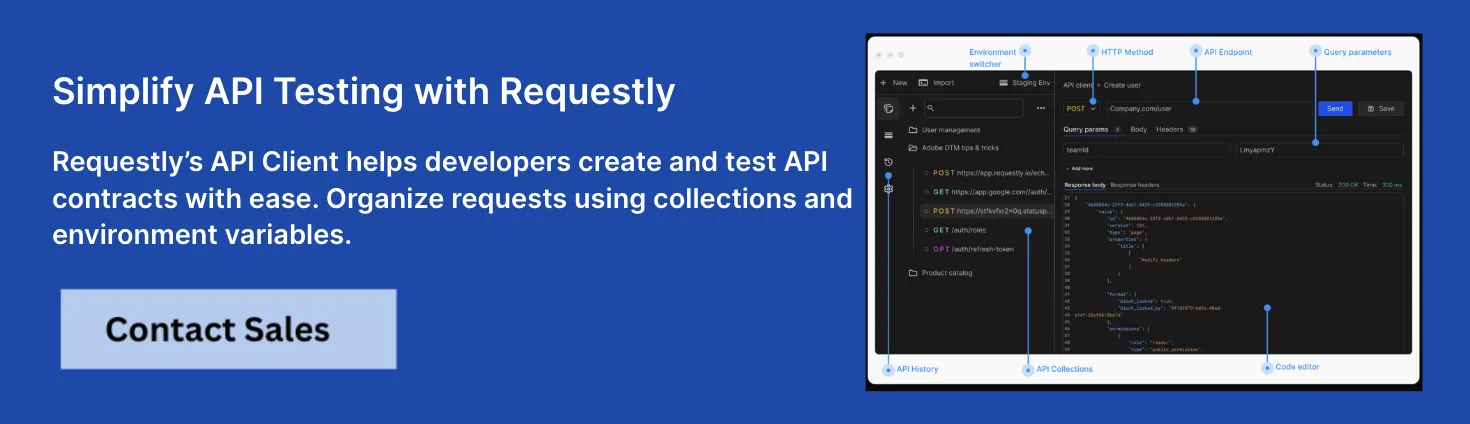
Integrate Requestly API Client for Efficient API Testing and Collaboration
Requestly API Client is an open-source, lightweight, and privacy-friendly tool designed for efficient API testing, debugging, and collaboration. Integrating it into your REST API development process offers numerous benefits that enhance productivity and collaboration:
- Organize API Requests with Collections: Group related API endpoints for streamlined testing and easy sharing among team members.
- Environment Variables: Manage and switch between multiple environments (development, staging, production) using reusable variables to avoid hardcoding values.
- Pre-request and Post-response Scripting: Automate workflows by adding JavaScript logic before requests are sent or after responses are received, such as dynamically setting headers or validating results.
- Support for Various Authorization Methods: Easily test APIs secured with API keys, OAuth 2.0, Basic Auth, and more.
- Collaborative Workspaces: Share API collections, environments, and session recordings in real-time within teams to improve transparency and accelerate feedback cycles.
- History and Replay: Keep a local log of sent API requests, making it easy to revisit and resend previous calls.
- Mock Server Capabilities: Simulate API endpoints for frontend development or testing scenarios where backend services are unavailable.
- Seamless Import/Export: Import existing collections, facilitating easy onboarding and migration.
- HTTP Request/Response Modification Rules: Intercept, modify, and test requests and responses on the fly by changing headers, bodies, or URLs.
- Session Recording and Debugging: Capture browser sessions, including network logs and console output, to help diagnose issues effectively.
Best Practices in REST API Design
Here are the key best practices to design efficient, scalable, and maintainable REST APIs:
- Use clear, consistent, and noun-based resource names in plural form, e.g., /users, /products
- Use HTTP methods appropriately: GET for reading data, POST for creating, PUT for updating, DELETE for removing resources
- Design intuitive and hierarchical URIs, nesting child resources under parent resources (e.g., /users/{id}/orders)
- Implement stateless communication where each request contains all information for processing without server-side sessions
- Use proper HTTP status codes to indicate request outcomes (e.g., 200 OK, 201 Created, 400 Bad Request, 404 Not Found, 500 Server Error)
- Support filtering, sorting, and pagination via query parameters for efficient data retrieval (e.g., /products?category=electronics&limit=10)
- Secure APIs using HTTPS, OAuth 2.0 or JWT, and implement input validation to prevent vulnerabilities
- Use versioning (URI versioning like /v1/users or header-based) to manage backward compatibility
- Provide comprehensive and interactive documentation using tools like OpenAPI/Swagger
- Optimize performance by implementing caching, compressing responses, and asynchronous processing
- Monitor and log API usage and health for continuous improvement and quick issue resolution
Conclusion
Designing a REST API with clear resource naming, correct HTTP methods, proper status codes, and robust security ensures it is easy to use, maintain, and scale. Incorporating caching, versioning, and thorough documentation further enhances performance and developer experience.
Additionally, using modern tools like the Requestly API Client streamlines API testing, debugging, and team collaboration, helping deliver reliable and high-quality APIs efficiently. These best practices and tools together pave the way for successful, scalable API development.

Contents
- Understanding REST API
- Setting Up the Development Environment
- 1. Install Node.js and npm
- 2. Create a Project Directory
- 3. Initialize the Node.js Project
- 4. Install Express and Other Dependencies
- 5. Set Up the Main Application File
- 6. Run and Test Your Server
- Creating a Simple REST API Step-by-Step
- 1. Setup Project
- 2. Install Express
- 3. Create Main Server File
- 4. Define RESTful Endpoints
- Integrate Requestly API Client for Efficient API Testing and Collaboration
- Best Practices in REST API Design
- Conclusion
Subscribe for latest updates
Share this article
Related posts
Get started today
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!