Website Accessibility Report: Components, Template & Tools

Learn what a website accessibility report includes, why it matters, and tools to create compliance-ready reports with actionable insights.
Millions of people rely on assistive technologies to navigate the web—yet many websites remain partially or entirely inaccessible. Whether it’s a missing image description or an unresponsive form, these issues create significant barriers for users with disabilities.
A website accessibility report plays a vital role in detecting and documenting such issues, offering a clear path toward building more inclusive digital experiences.
This article explores the importance of such reports and how they can improve accessibility and compliance.
What is a Website Accessibility Report?
A website accessibility report is a structured document that evaluates how well a website complies with accessibility standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines). It identifies accessibility issues that affect usability for individuals with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments and provides remediation guidance.
These reports combine automated scans, manual reviews, and real-device testing insights to offer a holistic picture of the website’s accessibility state.
Why is a Website Accessibility Compliance Report Important?
A website accessibility report is essential for the following specific reasons:
- Measurable accessibility status: It helps organizations understand their exact compliance level, highlighting both critical and hidden barriers across digital interfaces.
- Structured roadmap for remediation: The report outlines clear recommendations for fixing issues, making it easier for development teams to act.
- Risk mitigation: By identifying violations of standards like WCAG 2.1 or ADA, the report prevents potential lawsuits or regulatory penalties.
- Cross-functional alignment: It serves as a single source of truth for developers, designers, QA testers, and compliance teams to collaborate on accessibility goals.
- Demonstrable accountability: Regular reports show due diligence toward inclusive practices and are essential during audits or legal scrutiny.
Key Components of a Website Accessibility Report
Every effective accessibility report includes these critical components:
- Executive Summary: A brief overview of compliance status, key findings, and general severity distribution.
- Testing Methodology: Explanation of tools, techniques, scope, and types of testing conducted (automated, manual, assistive tech).
- Accessibility Violations: Detailed list of issues categorized by severity and corresponding WCAG criteria.
- Supporting Evidence: Screenshots, code snippets, and impacted URLs to validate the findings.
- Remediation Recommendations: Actionable suggestions for resolving each issue with technical or design fixes.
- Compliance Rating or Score: An overall accessibility rating that quantifies the site’s conformance.
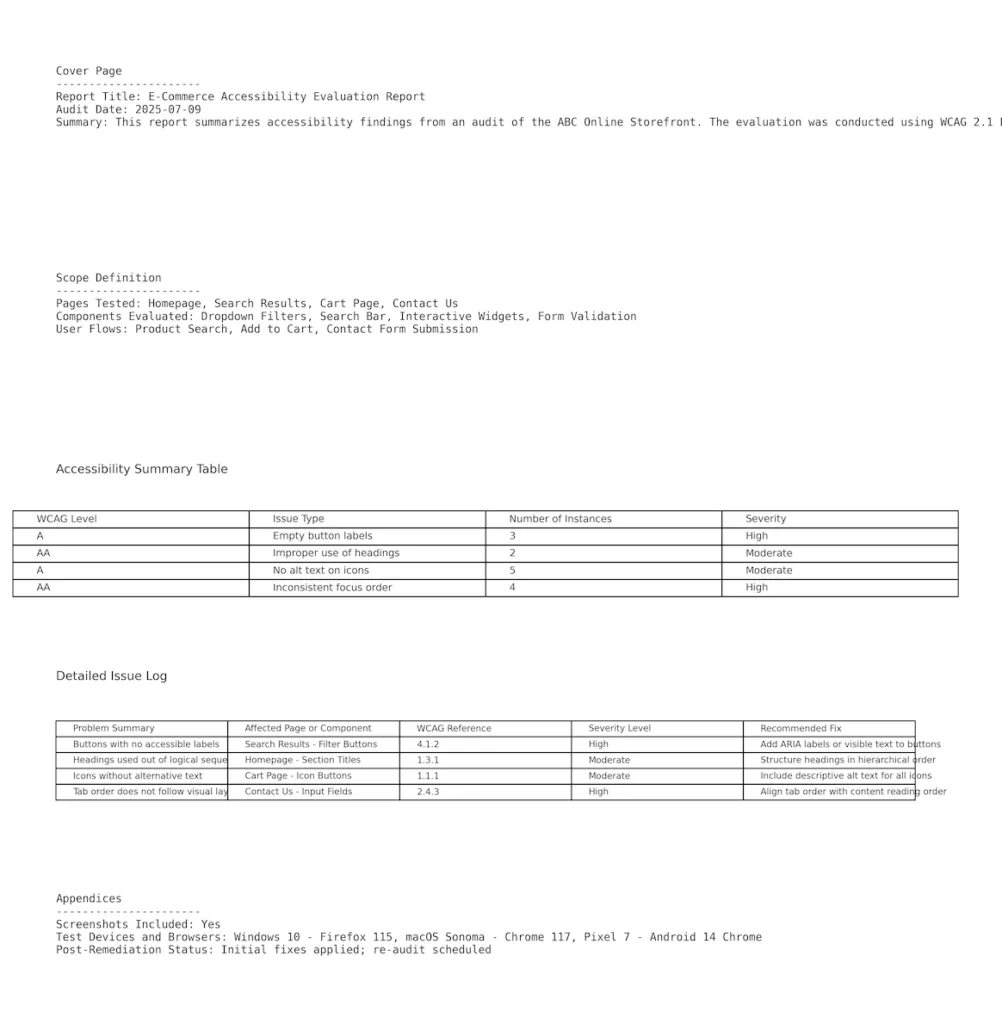
Website Accessibility Report Template and Examples
Standard accessibility report templates include:
- Cover Page with report title, date, and audit context
- Table of Contents for navigation
- Scope Definition (pages, components, user flows tested)
- Accessibility Summary Table (violations by category and WCAG level)
- Issue Detail Section with each problem broken down into:
- Issue Description
- Affected Page or Element
- WCAG Guideline Violated
- Severity
- Remediation Suggestion
- Appendices with screenshots, device/browser test info, and post-remediation status (if applicable)
Example of an Accessibility Report:
Who needs a Website Accessibility Report?
Organizations that directly engage users online benefit from accessibility reports, including:
- Web development agencies delivering client-ready digital products
- Corporate websites and SaaS platforms prioritizing inclusivity and compliance
- Public sector entities and universities bound by legal mandates
- E-commerce brands ensuring equal access to their product catalogs
- Legal, HR, and compliance teams tracking conformance across digital properties
When should you conduct a Website Accessibility Report?
Timing is key to ensuring accessibility issues are caught early and resolved efficiently. Here are the best times to run an accessibility report:
- During initial development or redesign: Integrate accessibility from the start to avoid costly rework later.
- Immediately after launch: Confirm that accessibility features are properly implemented before users encounter problems.
- On a recurring basis (quarterly or biannually): Regular assessments help maintain compliance and deliver a consistent, inclusive user experience.
- Before major public rollouts or announcements: Ensure your site is fully accessible during high-visibility campaigns to reach all audiences.
- In response to user complaints or legal concerns: Quickly identify and address specific issues to maintain trust and avoid potential legal risks.
How does a Website Accessibility Compliance Report work?
The following steps outline the process of creating a compliance-ready accessibility report:
- Define the audit scope: Identify specific pages, components, and workflows to test.
- Establish guidelines: Use WCAG 2.1 Level AA as the compliance benchmark.
- Conduct automated testing: Use tools like BrowserStack’s Accessibility Tool, or Lighthouse to quickly surface common violations.
- Perform manual checks: Validate keyboard navigation, focus indicators, ARIA usage, and screen reader behavior.
- Capture findings: Record each issue with evidence such as screenshots and DOM locations.
- Prioritize issues: Tag problems as critical, moderate, or minor to plan development resources accordingly.
- Suggest remediations: Offer precise code changes or design fixes for each violation.
- Compile the report: Format the document with all sections—from summary to technical details—and distribute it to stakeholders.
- Retest after fixes: Verify resolution and document improvements in an updated report.
Tools for Generating Website Accessibility Reports
Here is a list of top tools used to generate accessibility compliance reports:
1. BrowserStack
BrowserStack Accessibility offers a dedicated Web Accessibility Compliance Report solution designed for teams aiming to test at scale.
It helps validate WCAG conformance with in-depth audits integrated into cross-browser workflows.
Key Features:
- It offers automated accessibility audits
- Cross-device testing on real mobile and desktop environments
- Detailed violation reports mapped to WCAG success criteria
- Issue breakdown with severity tags and suggested fixes
- Screenshot and code reference capture for each error
- CI/CD integrations for continuous accessibility tracking
- Downloadable audit reports in accessible formats
2. Google Lighthouse
Google Lighthouse is a widely used tool for generating accessibility compliance reports directly in the browser. It helps developers perform quick audits that flag common WCAG 2.1 violations and generate structured reports useful for early-stage testing and documentation.
Key Features:
- Runs directly in Chrome DevTools or as a Node.js module
- Provides a numerical accessibility score out of 100
- Flags key WCAG 2.1 Level A/AA compliance issues
- Highlights focus management, color contrast, and ARIA problems
- Exports reports in HTML or JSON for compliance tracking
- Includes documentation links for each detected issue
3. Pa11y
Pa11y is a command-line tool purpose-built for automated accessibility compliance reporting. It integrates into development pipelines and produces machine-readable reports that help teams continuously monitor WCAG adherence across deployments.
Key Features:
- Supports automated testing for WCAG 2.0 and 2.1
- Generates structured reports in HTML and JSON formats
- Seamless integration with CI/CD tools like GitHub Actions or Jenkins
- Enables custom rule configuration for focused audits
- Categorizes issues by severity with clear DOM references
- Offers a dashboard to visualize accessibility trends over time
4. Tenon
Tenon is an API-first platform designed for large-scale, standards-based accessibility compliance auditing. It enables teams to automate report generation, pinpoint WCAG and Section 508 violations, and embed accessibility testing into the development lifecycle.
Key Features:
- API-driven testing for WCAG 2.0/2.1, Section 508, and custom standards
- Returns detailed issue data with fix suggestions and severity tagging
- Provides line and column references for each violation in code
- Easily integrates with CI/CD pipelines and development tools
- Includes browser plugins for on-the-fly audits
- Visual dashboards for tracking report outcomes across projects
Which tool to choose for Website Accessibility Compliance Report?
Choosing the right tool for generating a website accessibility compliance report depends on team needs, technical expertise, and reporting requirements.
Tools like Google Lighthouse, Pa11y, and Tenon offer useful insights through automated checks and CLI integrations. However, BrowserStack is recommended for real-device accuracy, visual context, and collaboration-friendly reporting.
BrowserStack Accessibility offers a dedicated Web Accessibility Compliance Report solution that helps teams ensure their websites meet WCAG standards across real browsers and devices. It simplifies the audit process, enables early detection of accessibility issues, and generates compliance-grade reports suitable for stakeholders, legal teams, and developers.
Common Accessibility Issues Highlighted in Reports
Here are some of the most commonly flagged accessibility violations, each described in practical terms:
- Missing alternative text: Images lack descriptive text, making them invisible to screen reader users.
- Unlabeled form elements: Inputs and buttons don’t have associated labels, causing confusion in form submissions.
- Inaccessible navigation menus: Menus can’t be reached or operated using a keyboard alone.
- Improper heading hierarchy: Pages skip heading levels, disrupting logical reading order for assistive tools.
- Non-descriptive link text: Generic links like “read more” offer no context, reducing usability.
- Focus indicator missing: Users navigating with a keyboard can’t see where they are on the page.
- Inconsistent ARIA roles: Incorrect use of ARIA attributes misguides assistive technologies.
- Lack of skip navigation links: Users can’t bypass repetitive content to reach the main area quickly.
- Dynamic content not announced: Changes like popups or form errors are invisible to screen readers.
- Low color contrast: Text blends into backgrounds, making it hard for visually impaired users to read.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Website accessibility reports must evaluate conformance against recognized legal standards, including:
- WCAG 2.1 (Level AA): The global benchmark for web accessibility, referenced in most regulations.
- ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act): U.S. law requiring digital accommodations for public services and businesses.
- Section 508: Applies to U.S. federal agencies and mandates that ICT (Information and Communication Technology) is accessible.
- EN 301 549: European standard that specifies accessibility requirements for digital products and services.
- AODA (Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act): Mandates accessible websites for public and private sectors in Ontario.
The accessibility report helps ensure the site complies with these laws by documenting adherence to each requirement.
Best Practices for Interpreting and Acting on the Report
Proper interpretation ensures the report drives meaningful accessibility improvements:
- Involve the entire product team: Developers, designers, QA, and content creators should review findings together.
- Focus on high-severity issues first: Prioritize fixes that block access or violate key WCAG principles.
- Turn recommendations into tickets: Use project management tools to assign and track resolution tasks.
- Conduct regression testing: Revalidate updated pages to ensure issues are fully fixed.
- Create internal guidelines: Standardize accessible design and development practices using the findings.
Conclusion
A website accessibility report goes beyond identifying issues and paves the way for digital inclusion. It enables organizations to create seamless, accessible experiences while adhering to global standards and legal requirements.
Whether launching a new site or optimizing an existing one, routine accessibility audits ensure ongoing usability for every user. Platforms like BrowserStack simplify this process by providing real-device testing, automation, and detailed compliance reporting, integrating accessibility seamlessly into each stage of development.

Contents
- Website Accessibility Report: Components, Template & Tools
- What is a Website Accessibility Report?
- Why is a Website Accessibility Compliance Report Important?
- Key Components of a Website Accessibility Report
- Website Accessibility Report Template and Examples
- Example of an Accessibility Report:
- Who needs a Website Accessibility Report?
- When should you conduct a Website Accessibility Report?
- How does a Website Accessibility Compliance Report work?
- Tools for Generating Website Accessibility Reports
- 1\. BrowserStack
- 2\. Google Lighthouse
- 3\. Pa11y
- 4\. Tenon
- Which tool to choose for Website Accessibility Compliance Report?
- Common Accessibility Issues Highlighted in Reports
- Legal and Compliance Considerations
- Best Practices for Interpreting and Acting on the Report
- Conclusion
Subscribe for latest updates
Share this article
Related posts