Running Ollama with Requestly – A guided tutorial


- Real LLM responses served locally
- Cloud-like API behavior
- No dependency on OpenAI or hosted endpoints
- Toggle between mock and real LLM responses instantly
Throughout the tutorial, screenshots and terminal outputs will be inserted to validate each step of execution, so readers can confidently follow along and verify their own environment.
1. Install & Verify Ollama Locally
http://localhost:11434
Install Ollama-
curl -fsSL https://ollama.ai/install.sh | sh
Pull the model-
ollama pull llama3.2:1b
Validate Ollama server is running
ps aux | grep ollama
/usr/local/bin/ollama serve
http://localhost:11434/
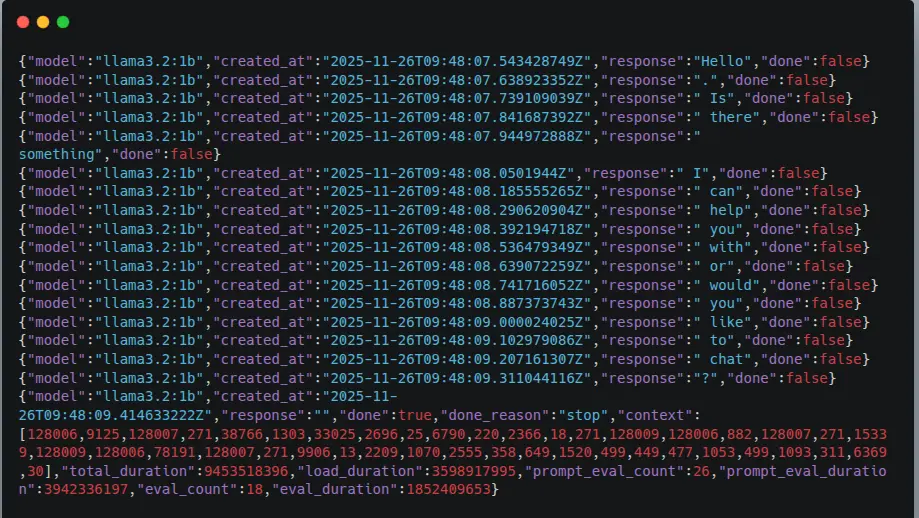
Test local inference via API
curl http://localhost:11434/api/generate -d '{
"model": "llama3.2:1b",
"prompt": "hello"
}'
2. Routing Local LLM Traffic via Requestly
To send LLM requests from a browser or external clients without modifying any application code, we use Requestly Redirect Rules.
This creates a cloud-like API endpoint while maintaining full local execution.
Create Redirect Rule
- Open Requestly
- Go to Rules from the left sidebar
- Click New Rule – Redirect Request
Fill in the configuration:
Field | Value |
Rule Type | Redirect Request |
IF - Request URL Contains | https://user1763230645199.requestly.tech/generate |
Redirect destination | http://localhost:11434/api/generate |
Rule Status | Enabled |
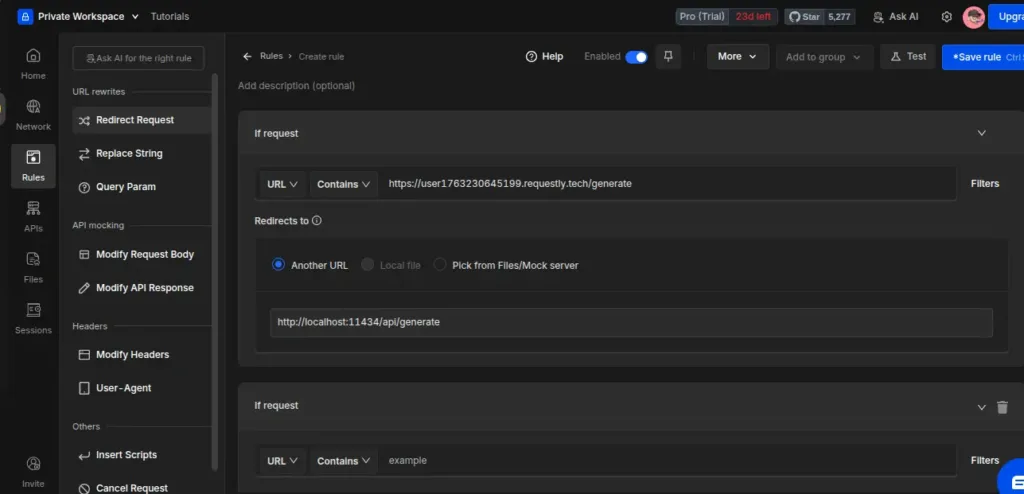
Here is the final working Redirect Rule configuration.
Also, this rule enables the full request flow:
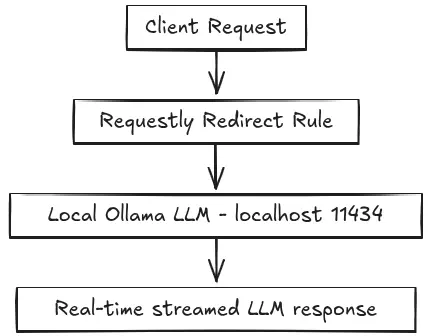
3. Test End-to-End Using Requestly API Client
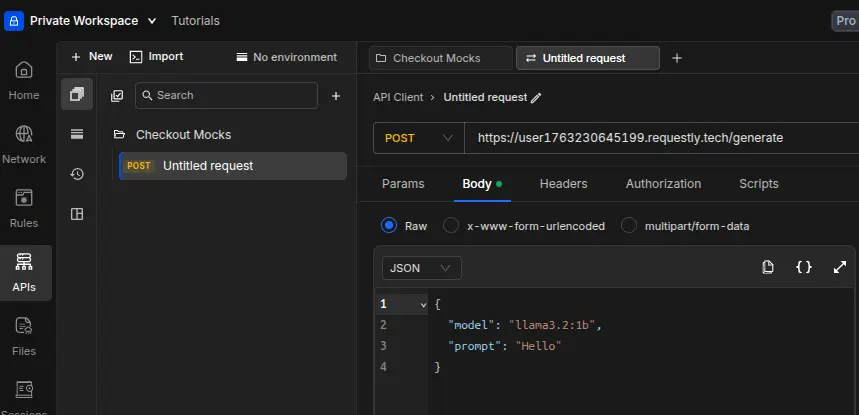
API Client Request
Inside Requestly – API Client:
- Method: POST
- URL:
https://user1763230645199.requestly.tech/generate
- Body (raw JSON):
{
"model": "llama3.2:1b",
"prompt": "Hello from Requestly"
}
Click Send.
You should see model tokens streaming back via local inference.
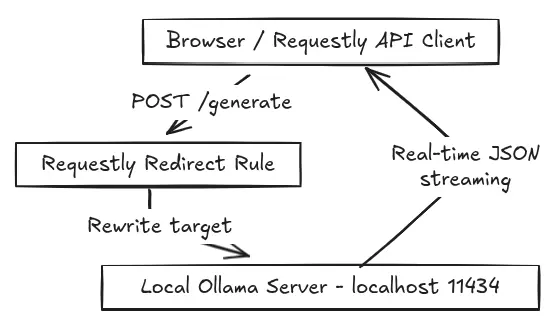
4. Final Working Architecture
Component | Responsibility |
Client (Browser / API Client / curl) | Sends prompt request |
Requestly | Redirects call to local model |
Ollama | Generates the LLM response |
Client | Receives streamed text |
Architecture Diagram
Why This Matters for Developers
Benefit | What it enables |
Local-first inference | No cloud dependency & offline-ready |
Zero code required | UI teams can test without waiting for the backend |
Privacy / Compliance | Data stays on the device |
Instant environment switching | Mock - Real model toggle |
Faster iteration | No API key, no rate limiting |
Conclusion
Running LLMs locally doesn’t require complex infrastructure or backend changes.
In our setup, Ollama handled the model execution entirely on the machine, while Requestly served as the routing layer, allowing us to forward API calls to the local inference endpoint without modifying any application code.
We validated the entire flow using only curl and the Requestly API Client, with a single Redirect Rule ensuring that every test request reached the llama3.2:1b model running on localhost. The integration worked smoothly end-to-end and demonstrated a practical workflow for secure, offline-ready AI development.
Any developer following these exact steps on Ubuntu can achieve the same result in one continuous run. This gives full control over where inference happens and makes it easy to adopt a local-first approach to modern LLM applications.

Contents
- 1. Install & Verify Ollama Locally
- Install Ollama-
- Pull the model-
- Validate Ollama server is running
- Test local inference via API
- 2. Routing Local LLM Traffic via Requestly
- Create Redirect Rule
- 3. Test End-to-End Using Requestly API Client
- API Client Request
- 4. Final Working Architecture
- Architecture Diagram
- Why This Matters for Developers
- Conclusion
Subscribe for latest updates
Share this article
Related posts