A Comprehensive Guide to API Client Libraries


Your lightweight Client for API debugging
No Login Required
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!










In an interconnected software ecosystem, applications rarely live in isolation. They depend on external APIs to communicate, exchange data, and perform critical functions. While APIs provide this connectivity, working with raw HTTP requests can quickly become cumbersome and error-prone.
To bridge this gap, API client libraries have emerged as the go-to solution. These libraries abstract away the low-level details of API communication, offering an easier, safer, and more developer-friendly interface for building integrations.
This guide explores the concepts, best practices, tools, and trends surrounding API client libraries, helping you understand why they matter and how to use them effectively.
What are API Client Libraries?
An API Client Library is a software package—often provided by API vendors—that simplifies communication between your application and an API. Instead of requiring developers to construct HTTP requests, manage headers, parse JSON, and handle responses manually, the library provides clean, language-specific functions and classes to perform these tasks automatically.
For example, instead of writing raw code to call an endpoint for a payment service, you could simply call paymentClient.createTransaction() from the client library. This abstraction saves time, reduces repetitive code, and minimizes human error.
Why use an API Client Library?
Using an API client library provides clear advantages that improve both developer experience and system reliability:
- An API client library makes development easier by allowing teams to focus on business logic rather than low-level networking details.
- It strengthens consistency by providing standardized methods and workflows across different projects.
- It reduces errors because response parsing, rate limiting, retries, and exception handling are managed by the library.
- It saves valuable development time by streamlining integrations with commonly used APIs.
- It increases security since most libraries include built-in features for handling authentication securely, such as OAuth flows or API keys.
API Client Library Architecture and Core Concepts
The architecture of an API client library typically contains several building blocks that work together to streamline communication:
- An abstraction layer converts low-level HTTP requests into high-level function calls.
- A dedicated authentication module manages tokens or credentials for secure access.
- Serialization and deserialization layers convert JSON or XML responses into language-specific objects.
- A structured error handling workflow ensures developers receive meaningful exceptions rather than raw error data.
- Version mapping guides the client library in pointing to appropriate API endpoints as versions evolve.
Programming Languages and Ecosystem Support for API Client Libraries
API client libraries exist in almost every programming ecosystem, and their effectiveness often depends on the language and its developer community:
- In JavaScript and TypeScript, client libraries are widely used for web APIs, with mature ecosystems built on tools like Axios.
- In Python, libraries are popular due to their simplicity and comprehensive support for REST and GraphQL APIs.
- In Java or C#, client libraries are valued in enterprise environments where type safety, scalability, and performance are paramount.
- In languages like Go and Rust, libraries are increasingly common for high-performance applications dealing with intensive API calls.
Authentication and Security in API Client Libraries
Security is a fundamental part of any integration, and API client libraries simplify it significantly:
- Most libraries manage API keys automatically by injecting them into request headers.
- They often support OAuth 2.0, with built-in token management and automatic refresh capabilities.
- Enterprise libraries may offer mutual TLS (mTLS) for highly secure communication with APIs.
- Many integrate with vaults or environment variables to prevent sensitive credentials from being exposed.
Error Handling and Reliability in API Client Libraries
A strong client library improves reliability by handling unexpected failures gracefully. Common practices include:
- Providing descriptive error classes that communicate exactly what went wrong.
- Enabling automatic retries with backoff mechanisms to reduce downtime caused by temporary errors.
- Managing rate-limit responses by queuing or adjusting request frequency.
- Offering diagnostic logging tools so developers can easily identify problems in their integrations.
Performance Optimization for API Client Libraries
Well-designed libraries help applications scale better by introducing performance optimizations such as:
- Using connection pooling to reuse HTTP connections and reduce latency.
- Allowing batching of multiple requests into consolidated network calls.
- Providing caching mechanisms to avoid redundant requests for frequently accessed resources.
- Supporting streaming of large responses so applications can process data incrementally instead of all at once.
Design Best Practices for API Client Libraries
A client library’s usefulness often depends on how well it is designed. The best libraries share these traits:
- They offer an intuitive interface with function names and workflows that are clear to developers.
- They ensure consistency across methods so that error handling and call structures feel predictable.
- They remain extensible by offering settings and options without cluttering core functionality.
- They support self-documentation with structured code and inline developer hints.
Documentation and Developer Experience in API Client Libraries
Documentation can make or break the adoption of a client library. Strong developer experience usually comes from:
- Providing setup guides with practical, language-specific examples.
- Offering detailed reference documentation with methods, parameters, and return types.
- Including interactive examples or sandboxes that allow developers to test quickly.
- Building a community through forums, GitHub repositories, and shared developer conversations.
Testing and Debugging API Client Libraries
Testing and debugging ensure that libraries remain reliable through real-world usage:
- Developers rely on unit tests built on mock APIs to validate functions without hitting production.
- Integration tests confirm full workflows between the client library and the actual API service.
- Debugging tools such as verbose logs, request traces, and response dumps simplify error analysis.
- Libraries often provide safe defaults that ensure failures are captured explicitly rather than missed silently.
Versioning and Backward Compatibility in API Client Libraries
Since APIs evolve, managing versions carefully is a vital part of client library design:
- Libraries typically follow semantic versioning to signal backward-compatible and breaking changes.
- Migration guides help developers transition smoothly to new versions.
- Compatibility layers ensure existing applications don’t break unexpectedly when libraries evolve.
- Deprecation warnings inform developers proactively when certain functions or methods are being retired.
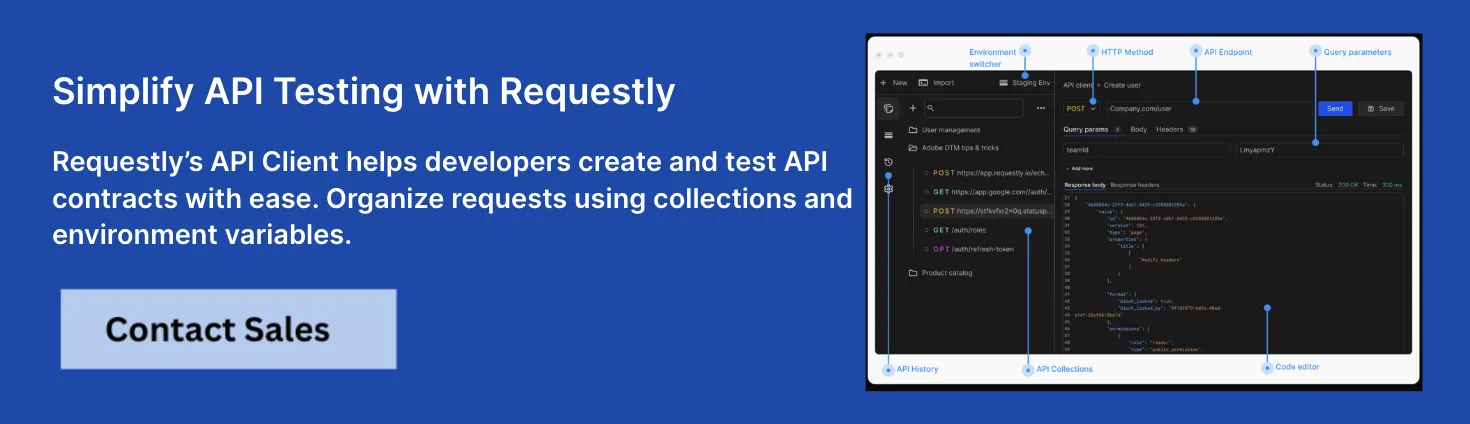
Why choose Requestly?
While API client libraries simplify communication with APIs, developers often face challenges in testing, debugging, and simulating real-world scenarios. This is where the Requestly API Client becomes a valuable companion. It extends the capabilities of traditional client libraries by ensuring developers can build, test, and debug more effectively.
- The Requestly API Client allows developers to mock APIs so integrations can be built even before the actual backend service is available.
- It provides built-in features to modify requests and responses, enabling comprehensive testing of error handling, authentication flows, and edge cases.
- It enhances collaboration within teams by allowing mock APIs, traffic rules, and debugging setups to be shared seamlessly.
- It supports multiple API communication styles—REST, GraphQL, and gRPC—making it a versatile client tool for modern development environments.
Conclusion
API client libraries are critical components of modern software development. They simplify complex workflows, secure communication, minimize errors, and boost performance. From authentication to backward compatibility, they serve as a foundation for seamless API adoption.
As APIs continue to dominate technology, understanding how to use and design client libraries effectively is essential for developers across all industries. Tools like Requestly further enhance the workflow by enabling rapid testing, debugging, and optimization, ultimately accelerating development and improving reliability.

Contents
- What are API Client Libraries?
- Why use an API Client Library?
- API Client Library Architecture and Core Concepts
- Programming Languages and Ecosystem Support for API Client Libraries
- Authentication and Security in API Client Libraries
- Error Handling and Reliability in API Client Libraries
- Performance Optimization for API Client Libraries
- Design Best Practices for API Client Libraries
- Documentation and Developer Experience in API Client Libraries
- Testing and Debugging API Client Libraries
- Versioning and Backward Compatibility in API Client Libraries
- Why choose Requestly?
- Conclusion
Subscribe for latest updates
Share this article
Related posts
Get started today
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!