Top API Virtualization Tools Comparison: Which to choose?

Your lightweight Client for API debugging
No Login Required
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!










API virtualization plays a crucial role in modern development pipelines by decoupling teams from unavailable or evolving backend services. According to SmartBear’s 2024 API survey, over half of development teams rely on service virtualization to eliminate dependency-related bottlenecks. The right tool helps teams prototype, test, and release faster without relying on unstable or costly APIs.
This guide compares top API virtualization tools in-depth, including their core features, strengths, limitations, and the use cases where each performs best.
What is API Virtualization?
API virtualization is a technique for simulating API endpoints and their behaviors without relying on the actual backend systems. These simulated services—often called virtual APIs or mocks—emulate the responses of real services under various conditions.
Teams can simulate slow responses, authentication failures, or specific data payloads, allowing for realistic testing and development even before the real APIs exist.
Why use API Virtualization Tools?
Service virtualization tools bring significant benefits to development and testing processes:
- Faster testing and development cycles
- Independent parallel work for frontend/backend
- Safe simulation of third-party or rate-limited APIs
- Testing for edge cases like latency, timeouts, or 500 errors
- Cost-effective environments for QA, staging, and demos
How do API Virtualization Tools Work?
Most API virtualization tools intercept HTTP or protocol-level traffic and return mock responses. These responses may be static or dynamic and can be customized based on request patterns, query parameters, or headers.
Some tools support importing API specifications (OpenAPI, RAML, WSDL) and auto-generating mocks. Others allow for detailed scripting or logic injection to simulate more realistic, stateful behavior.
When to use API Virtualization in Development and Testing?
API virtualization is ideal for:
- Developing or testing when the actual APIs are not available
- Replacing unstable or costly third-party services during test cycles
- Simulating rare or error-prone scenarios for robust QA
- Parallelizing frontend and backend workflows
- Setting up isolated test/demo environments with controlled behavior
Key Criteria for Comparing API Virtualization Tools
When evaluating tools, consider the following critical aspects:
- Protocol and API Specification Support: Support for REST, SOAP, GraphQL, and the ability to import OpenAPI or WSDL definitions ensures broader compatibility.
- Ease of Setup and Use: User-friendly GUIs or intuitive CLI workflows can accelerate onboarding and daily usage.
- Mocking Capabilities: Important to assess whether the tool supports static responses, dynamic logic, or stateful simulations.
- Integration with CI/CD Pipelines: CLI tools, Docker support, or direct integrations help embed virtualization into your deployment and testing workflows.
- Performance and Scalability: Look for tools that can handle concurrent requests, simulate latency or throttling, and scale in test environments.
- Security and Access Control: SSL support, authentication, and permission management are important for use in staging or shared environments.
- Licensing and Cost: Teams should assess open-source options, free tiers, or enterprise pricing based on scale and required features.
Top API Virtualization Tools Compared
Below is a detailed breakdown of the most widely used tools, including what each is, its key features, strengths, limitations, and ideal use cases.
1. MockServer
What it is:
MockServer is an open-source API mocking tool built in Java that supports HTTP and HTTPS service virtualization. It can be deployed locally, in Docker containers, or embedded into test suites.
Key Features:
- Programmatic mocks via Java or JSON
- Support for request verification and response templating
- Ability to proxy traffic and override live API behavior
- Dockerized deployment for CI pipelines
Strengths: Highly configurable with automation support, proxying, and strong verification capabilities.
Limitations: No GUI; scripting knowledge required.
Best for: Backend or DevOps teams comfortable with Java or automation frameworks.
2. WireMock
What it is:
WireMock is a flexible Java-based API simulation tool supporting both standalone servers and embedded configurations. It can simulate REST and SOAP APIs and emulate stateful interactions.
Key Features:
- Dynamic stubbing and request matching
- Stateful behavior simulation
- JSON-based config and Java DSL
- Fault injection (timeouts, delays, etc.)
- WireMock Cloud for hosted solutions
Strengths: Excellent control over behavior; strong Java ecosystem integrations; broad protocol support.
Limitations: Steeper learning curve; advanced use cases require coding.
Best for: QA automation and complex integration testing in Java-based environments.
3. Postman Mock Server
What it is:
Part of the Postman ecosystem, Mock Server allows teams to create and share REST API simulations using Postman collections and environments.
Key Features:
- Mock endpoints from Postman collections
- Environment variables for dynamic values
- Integration with automated test suites
- Public and private mock URL options
Strengths: Extremely simple to use; ideal for Postman users; requires no additional infrastructure.
Limitations: Limited to REST APIs; advanced logic requires higher-tier plans.
Best for: Quick prototyping, frontend-backend collaboration, and lightweight mocks.
4. Mockoon
What it is:
Mockoon is a desktop-based open-source API mocking tool that supports REST APIs with an intuitive GUI and local-first development philosophy.
Key Features:
- GUI for local mock server creation
- Response rules based on request patterns
- Environment and route management
- No-code response editing
- CLI runner for CI integration
Strengths: Extremely fast to set up; great for local development and manual testing.
Limitations: No cloud or multi-user support; limited dynamic logic.
Best for: Solo developers, frontend engineers, or quick local mock setups.
5. Traffic Parrot
What it is:
Traffic Parrot is an enterprise-grade service virtualization platform supporting REST, SOAP, JMS, and other legacy systems, designed for large teams and regulated environments.
Key Features:
- Virtualization of HTTP, JMS, and TCP services
- Contract testing support
- Integration with CI/CD and test frameworks
- Recording and replaying real API traffic
- Scriptable mocks and delay injection
Strengths: Enterprise focus; legacy protocol support; designed for complex test environments.
Limitations: Paid-only solution; more complex to set up.
Best for: Enterprises dealing with legacy systems and high-compliance requirements.
Comparison Table: Feature-by-Feature Breakdown
This table compares the features of the top API virtualization tools:
Tool | REST | SOAP | Dynamic Mocking | CI/CD Integration | Cloud Support | Cost |
MockServer | yes | no | yes | yes | no | Free |
WireMock | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | Free + Paid |
Postman Mocks | yes | no | limited | yes | yes | Free + Paid |
Mockoon | yes | no | yes | no | no | Free |
Traffic Parrot | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | Paid |
How to choose the Right Tool for your Project?
Here’s a detailed guide on how to choose the right API virtualization tool:
1. Define Your Use Case
Start by identifying why you need API virtualization. Different tools serve different goals.
- Frontend-backend parallel development: Tools like Postman Mocks or Mockoon can help rapidly simulate REST APIs with minimal setup.
- Automated integration testing: Tools like WireMock and MockServer offer scriptable, programmable mocks suitable for pipelines.
- Service virtualization for legacy systems: Enterprise tools like Traffic Parrot support SOAP, JMS, or proprietary protocols.
- Debugging and inspection: Tools like Requestly help with intercepting traffic and testing live changes.
2. Evaluate Protocol and Specification Support
Your tool must be compatible with the types of APIs you’re working with.
- REST and OpenAPI: Most tools support this out of the box.
- SOAP and WSDL: Requires tools like WireMock or Traffic Parrot.
- GraphQL or gRPC: Fewer tools offer native support—check extensibility or plugin systems.
- Protocol transformations: Needed if your systems consume APIs in multiple formats.
3. Assess Mocking Capabilities
Different teams require different levels of mocking complexity.
- Static mocks: Good for simple use cases and frontend development.
- Dynamic mocks: Needed for simulating different responses based on query, headers, or payloads.
- Stateful mocks: Useful for login flows, session handling, or workflows.
- Fault simulation: Simulate timeouts, rate limiting, or 5xx responses to test error handling.
4. Consider Team Skills and Workflow
The tool should align with the skill level and preferred workflows of your team.
- GUI-based tools like Mockoon or Postman are easier for non-developers or frontend teams.
- Scriptable tools like MockServer or WireMock are better for test automation and DevOps-heavy teams.
- Collaborative tools like Requestly offer workspace sharing and browser-based access.
5. Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Automation is essential in modern development environments.
- Look for CLI support, Docker containers, or REST APIs for spinning up mocks during test runs.
- Ensure compatibility with your CI tools (Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI).
- Tools should allow automatic deployment and cleanup to maintain clean pipelines.
6. Determine Hosting Needs
Decide whether you need a local, cloud, or hybrid deployment model.
- Local tools are fast and good for individual development (e.g., Mockoon, MockServer).
- Cloud tools allow sharing, centralized environments, and multi-user setups (e.g., Requestly, Postman Cloud).
- Hybrid tools offer both, and are best for flexible team setups (e.g., WireMock with Docker and cloud add-ons).
7. Analyze Security and Governance
Mock services, especially in shared environments, must be secure.
- Support for authentication (API keys, OAuth) is important.
- Tools should offer RBAC (role-based access control) in multi-user setups.
- SSL/TLS, audit logs, and access expiration add protection in regulated industries.
8. Review Licensing and Cost Structure
Ensure the tool fits your budget and scales with your usage.
- Open-source options like MockServer, Mockoon, and WireMock (self-hosted) are cost-effective but may require more setup.
- Freemium models like Postman are ideal for small teams.
- Enterprise tools like Traffic Parrot offer advanced features but come at a premium.
- Consider how the tool charges—per user, per endpoint, or by usage volume.
9. Examine Community and Support
Strong community and documentation reduce ramp-up time and future blockers.
- Look for active GitHub repos, forums, or Slack communities.
- Premium tools should offer dedicated support, onboarding, and SLA guarantees.
- Check for API documentation and sample projects to reduce trial-and-error.
10. Pilot and Benchmark Before Committing
Before adopting a tool organization-wide:
- Run a proof of concept with a critical API or test suite.
- Compare latency, setup time, and ease of use across team roles.
- Validate integration with existing tooling (API gateways, test frameworks, CI/CD).
Pro Tip: For teams looking for fast, browser-native mocking and debugging, the Requestly API Client is a lightweight but powerful option. It enables developers and testers to instantly create mock APIs, intercept requests, and simulate live changes—all from the browser, without any backend setup.
Common Challenges in Adopting API Virtualization Tools
While API virtualization can accelerate development and testing, its implementation comes with practical hurdles that teams should be prepared for. Addressing these challenges early ensures smoother integration and better ROI from the tools used.
- Learning curve for complex tools: Tools like WireMock or MockServer require scripting knowledge, DSLs, or understanding of HTTP protocols. This can be a barrier for teams without prior experience in test automation or backend configuration.
- Keeping mocks in sync with live APIs: As APIs evolve, mock definitions can become outdated, leading to false positives or missed edge cases during testing. Without a strong version control strategy, teams risk relying on inaccurate simulations.
- Overhead of maintaining complex scenarios: Stateful or conditional mocks—such as login workflows or token validation—require continuous updates. Without automated tooling or dedicated ownership, these mocks degrade over time.
- Fragmented environments: In the absence of centralized tools or shared repositories, different teams may create and maintain their own mocks independently, causing inconsistency across dev, test, and staging environments.
- Lack of stakeholder buy-in: In organizations where frontend, backend, and QA teams work in silos, there may be low adoption of virtualization tools unless clear benefits are communicated across roles.
Best Practices for Using API Virtualization Effectively
To fully harness the benefits of API virtualization, teams should establish structured practices that keep mocks reliable, scalable, and aligned with business goals. The following best practices can improve maintainability and increase test coverage.
- Maintain versioned mocks alongside API definitions: Store mock configurations in the same repository as the OpenAPI/Swagger specs to keep them in sync with actual API changes. This allows traceability and rollback if inconsistencies are introduced.
- Use environment-specific mocks for dev, QA, and staging: Tailor mock data and behavior to simulate real-world conditions relevant to each environment. For example, a dev environment might use simplified payloads, while staging simulates production latency.
- Automate mock deployment in CI/CD pipelines: Integrate mock server spin-up and teardown as part of your automated test suites. This ensures consistency, reduces manual overhead, and allows repeatable tests across builds.
- Simulate network faults and edge cases: Go beyond 200 OK responses—mock 401 errors, 500 failures, rate limits, and timeouts to ensure that systems handle failures gracefully under real-world conditions.
- Involve developers, testers, and DevOps equally: API virtualization works best when shared across roles. Developers can define mocks, testers can expand edge cases, and DevOps can automate deployments—creating a full lifecycle feedback loop.
- Document mocks as part of your API contracts: Treat mocks as test artifacts and include them in documentation, especially when onboarding new teams or integrating with third-party consumers.
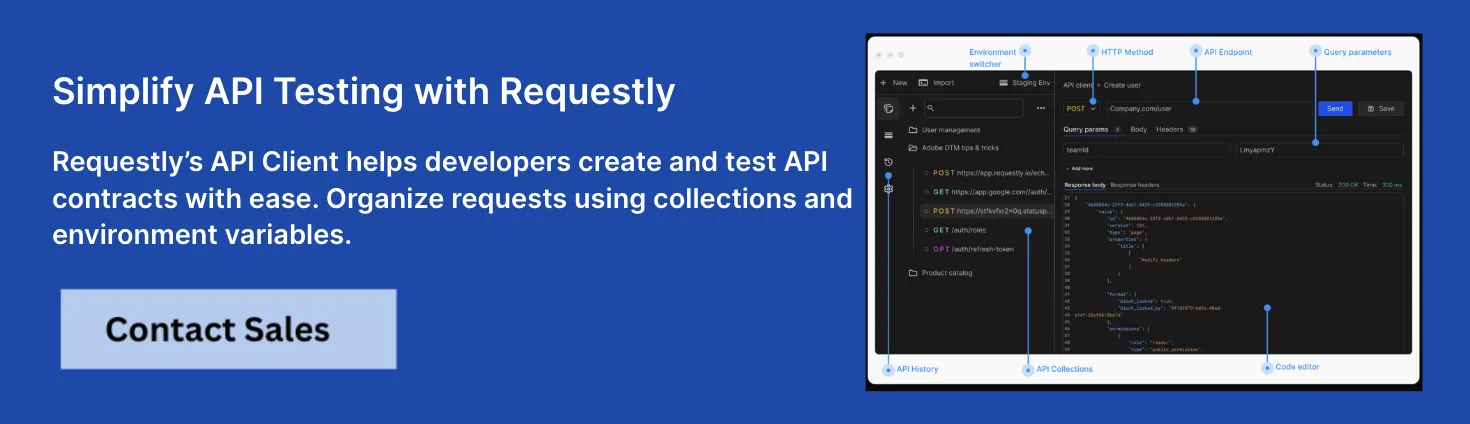
Requestly API Client for Mocking and Debugging
One of the most developer-friendly tools for browser-based API simulation and debugging is the Requestly API Client.
What it is:
Requestly API Client is a powerful tool that lets developers mock APIs, intercept HTTP(S) requests, and simulate real-world API behavior—all from the browser.
Key Features:
- Mock API Creation: Easily define endpoints and simulate RESTful API responses with JSON, headers, and status codes.
- Intercept and Modify Traffic: Debug and test how frontend applications behave under different network or API conditions.
- No Setup Required: Operates entirely in-browser—no backend or infrastructure needed.
- Collaborative Workspaces: Share mocked APIs with team members for consistent testing environments.
- Advanced Rule Engine: Modify requests and responses dynamically, redirect URLs, or inject headers.
- Secure Testing: Runs locally with no need to expose test data to the cloud.
Why it stands out:
Requestly fills a critical gap by enabling non-disruptive, low-code API testing for developers and QA engineers who want fast feedback without heavy setups. It’s especially useful in frontend-heavy workflows or when rapid prototyping is essential.
For modern teams needing full control over network behavior without managing heavy tooling, Requestly API Client offers a sleek, fast, and effective solution.
Conclusion
API virtualization tools offer significant benefits across development, testing, and integration cycles. From lightweight desktop tools to enterprise-grade simulation platforms, the choice depends on team needs, protocol coverage, complexity, and budget.
While tools like WireMock and Traffic Parrot are ideal for complex, enterprise scenarios, others like Mockoon and Postman Mocks provide simplicity for day-to-day use. For developers looking for a seamless and browser-first experience, Requestly API Client delivers unmatched flexibility and usability.
By adopting the right tool and integrating it into CI/CD workflows, teams can minimize delays, simulate complex scenarios, and ship faster with higher confidence.

Contents
- What is API Virtualization?
- Why use API Virtualization Tools?
- How do API Virtualization Tools Work?
- When to use API Virtualization in Development and Testing?
- Key Criteria for Comparing API Virtualization Tools
- Top API Virtualization Tools Compared
- 1. MockServer
- 2. WireMock
- 3. Postman Mock Server
- 4. Mockoon
- 5. Traffic Parrot
- Comparison Table: Feature-by-Feature Breakdown
- How to choose the Right Tool for your Project?
- Common Challenges in Adopting API Virtualization Tools
- Best Practices for Using API Virtualization Effectively
- Requestly API Client for Mocking and Debugging
- Conclusion
Subscribe for latest updates
Share this article
Related posts
Get started today
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!