Build GraphQL APIs with MongoDB: Setup, Schema, Resolvers, and Best Practices

Your lightweight Client for API debugging
No Login Required
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!










Combining GraphQL and MongoDB brings modern APIs greater flexibility, real-time data access, and enhanced performance. This integration streamlines data handling and empowers applications to efficiently manage large, dynamic datasets for both querying and updates.
This article walks through each step of integrating GraphQL with MongoDB, from setting up the environment and defining schemas to handling advanced usage scenarios, deploying securely, and streamlining API testing.
What is GraphQL and MongoDB?
GraphQL is a strongly-typed query language and server-side runtime for APIs, allowing clients to request precisely the data they need in a single call. It defines a schema that outlines how data can be queried, ensuring that responses are predictable and tightly controlled. GraphQL supports queries, mutations for modifying data, and subscriptions for real-time updates, making it flexible for modern web application needs.
MongoDB is a leading NoSQL database known for its flexibility, horizontal scalability, and JSON-like document storage. Developers use MongoDB to store large volumes of dynamic, semi-structured data, enabling rapid changes to application data models without rigid schemas.
Combining GraphQL with MongoDB allows applications to efficiently retrieve, modify, and subscribe to real-time data, powering responsive APIs that scale with evolving business requirements.
Setting Up the Environment
Begin by preparing a development environment with the essential tools to integrate GraphQL with MongoDB. The most common stack includes Node.js for the server runtime, Express as the application framework, GraphQL for API design, and Mongoose as the MongoDB object modeling library.
- Node.js & npm: Ensure Node.js and npm are installed for managing dependencies and running the server.
- MongoDB: Install and run a local MongoDB database, or use a cloud-based service like MongoDB Atlas.
- Required Libraries: Use npm or yarn to install Express, graphql, apollo-server-express, and mongoose.
- Project Initialization: Initialize your project directory with npm init or yarn init, then install all necessary dependencies for backend development.
This setup provides a robust foundation for building, querying, and managing a GraphQL API backed by MongoDB.
Defining the MongoDB Schema with Mongoose
Mongoose provides a powerful schema-based solution to define the structure of documents within a MongoDB collection. A schema outlines the fields, their data types, validation rules, default values, and other constraints that each document must follow.
To define a schema, use Mongoose’s Schema constructor, specifying the fields and their properties. For example:
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: { type: String, required: true },
email: { type: String, unique: true, lowercase: true },
age: { type: Number, min: 18 },
createdAt: { type: Date, default: Date.now }
});
After defining the schema, create a model using mongoose.model(), which provides an interface for CRUD operations on the corresponding MongoDB collection. This setup enforces data integrity and consistency while interacting with MongoDB.
Creating the GraphQL Schema
A GraphQL schema is the blueprint of your API, defining the types of data that clients can query or modify. It specifies the structure of the data, available queries, mutations for data modifications, and subscriptions for real-time updates. The schema is written using GraphQL’s Schema Definition Language (SDL) and outlines the relationships between different object types.
For example, a typical schema might define a User type with fields like name and email along with associated queries and mutations:
type User {
id: ID!
name: String!
email: String!
}
type Query {
getUser(id: ID!): User
getUsers: [User]
}
type Mutation {
createUser(name: String!, email: String!): User
}
This schema helps clients know exactly what data can be requested or updated, enabling precise and efficient interactions with the backend without exposing implementation details. The schema forms the foundation for building resolvers that connect data sources like MongoDB to GraphQL queries and mutations.
Connecting GraphQL to MongoDB
Connecting GraphQL to MongoDB involves implementing resolvers that bridge the GraphQL schema with the MongoDB database. Resolvers contain the logic to fetch and manipulate data in response to GraphQL queries and mutations.
Typically, a GraphQL server is set up using libraries like Apollo Server or express-graphql, and Mongoose is used to interact with MongoDB. For each query or mutation, the resolver calls Mongoose methods to perform CRUD operations directly on MongoDB collections.
const resolvers = {
Query: {
getUser: async (_, { id }) => {
return await UserModel.findById(id);
},
getUsers: async () => {
return await UserModel.find({});
}
},
Mutation: {
createUser: async (_, { name, email }) => {
const newUser = new UserModel({ name, email });
return await newUser.save();
}
}
};
This approach efficiently connects the GraphQL API with MongoDB, enabling flexible data querying and manipulation while maintaining the strong typing and validation offered by GraphQL and Mongoose.
Handling Advanced Scenarios
When integrating GraphQL with MongoDB, several advanced scenarios arise that help optimize performance and improve developer experience:
- Pagination and Filtering: Implement pagination techniques such as cursor-based or offset-based pagination to efficiently handle large datasets. Filtering allows clients to query data based on specific criteria, improving relevance and reducing data transfer.
- Error Handling and Validation: Incorporate proper error handling within resolvers to catch and communicate database or validation errors to clients gracefully, ensuring robust API behavior.
- Optimizing with Data Loaders: Use tools like DataLoader to batch and cache database requests, preventing repetitive queries and reducing the N+1 query problem common in nested GraphQL queries.
- Complex Queries and Aggregation: Leverage MongoDB’s aggregation framework for complex data processing and transformations, exposing these capabilities through custom GraphQL schema fields or resolvers.
- Authentication and Authorization: Secure the API by implementing middleware or resolver-level checks to enforce user permissions and protect sensitive data.
These advanced techniques ensure that the GraphQL-MongoDB API remains performant, secure, and scalable in real-world applications.
Deployment and Best Practices
Deploying a GraphQL API backed by MongoDB requires careful attention to environment configuration, security, and performance:
- Environment Configuration: Use environment variables to manage sensitive information such as database URIs and API keys, keeping them out of the codebase.
- Security Practices: Enforce authentication and authorization, enable HTTPS, and sanitize inputs to protect against injection attacks and unauthorized access.
- Performance Optimization: Implement efficient indexing in MongoDB, use query optimization techniques, and enable caching where applicable to reduce latency.
- Error Monitoring and Logging: Integrate monitoring tools to track errors, performance metrics, and API usage, facilitating quicker troubleshooting and maintenance.
- Scalability: Design schemas and resolvers keeping scalability in mind, considering shard keys for large MongoDB clusters and optimizing GraphQL queries.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive API documentation to aid developers and ensure the API remains understandable and maintainable.
Following these best practices helps deliver a secure, efficient, and maintainable GraphQL API that scales well in production environments.
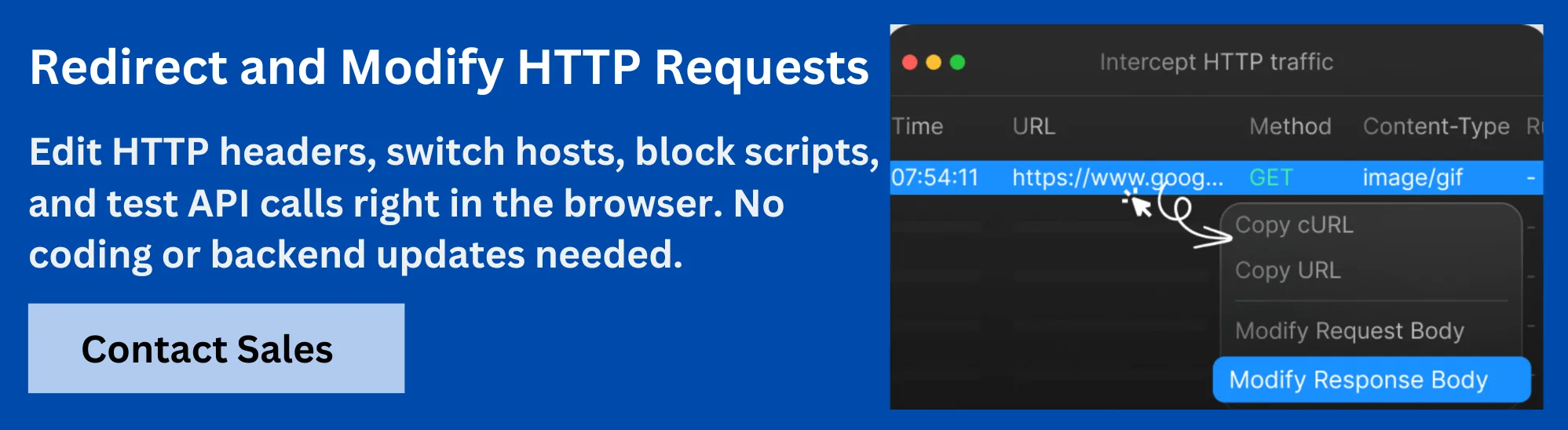
Boost API Testing and Debugging with Requestly HTTP Interceptor
Requestly HTTP Interceptor is a versatile tool that empowers developers to intercept, modify, and mock HTTP and GraphQL requests in real-time. It offers precise control by filtering GraphQL operations by name, enabling dynamic request and response modifications using custom JavaScript.
Key capabilities include:
- Simulating API delays and network conditions for thorough testing
- Modifying request and response payloads without backend changes
- Redirecting API calls across environments seamlessly
- Injecting scripts for advanced debugging and scenario testing
Requestly by BrowserStack accelerates frontend development by decoupling it from backend dependencies, simplifies debugging, and helps test edge-case scenarios effectively, ensuring high-quality API integrations with GraphQL and MongoDB.
Conclusion
Integrating GraphQL with MongoDB offers a powerful combination for building flexible, scalable, and efficient APIs. By carefully designing schemas, implementing resolvers, and handling advanced scenarios such as pagination and error management, developers can deliver rich data experiences tailored to client needs.
Adopting best practices around deployment, security, and performance optimization ensures that your API remains robust and reliable in production environments. Tools that enhance testing and debugging further accelerate development, helping teams maintain high-quality code and rapid iteration.
Harnessing these strategies equips developers to build modern, responsive, and maintainable APIs that can scale with evolving business requirements.

Contents
Subscribe for latest updates
Share this article
Related posts
Get started today
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!