302 Temporary Redirect: What It Is & How to Use It


Your lightweight Client for API debugging
No Login Required
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!










Temporary redirects play a crucial role in web management by directing users to different URLs without making permanent changes. Among these, the 302 Temporary Redirect is widely used to signal that a web resource is temporarily located elsewhere.
This article explores the ins and outs of 302 redirects, from their technical mechanism and key differences with permanent redirects to practical use cases and SEO considerations. It also covers how to implement and manage 302 redirects effectively across various platforms and the best practices to avoid common pitfalls.
What Is a 302 Temporary Redirect?
A 302 Temporary Redirect is an HTTP status code that informs browsers and search engines that a requested resource has been temporarily moved to a new URL.
Unlike a permanent redirect (HTTP 301), a 302 redirect tells clients that the original URL will be used again in the future, and the content at the new location is just a temporary substitute. When a server responds with a 302 status, it includes a Location header with the temporary destination URL, prompting browsers to redirect users seamlessly.
How 302 Redirects Work
The functioning of 302 redirects involves redirecting users without them realizing the change in URLs. When a user requests a webpage, the server responds with an HTTP 302 status code and a Location header specifying the temporary destination. Upon receiving this, browsers immediately make a new request to the provided URL. Typically, any POST method changes to GET during this process, adhering to HTTP standards, which makes the redirect seamless and temporary from the user’s view.
Key Differences: 302 vs. 301 Redirects
To understand the different roles these redirects play, consider the following points:
- 301 redirects indicate a permanent move, signaling that the original URL should be replaced in indexes.
- 302 redirects signify a temporary move, so the original URL is retained in indexes.
- 301 redirects pass full SEO value (link equity) to the new URL, while 302 redirects generally do not transfer SEO value since the move is not permanent.
- Though both redirect users transparently, 301s update search engine indices more definitively.
Common Use Cases for 302 Redirects
The following examples demonstrate scenarios where 302 redirects are appropriate due to their temporary nature:
- Redirecting users from a page undergoing maintenance or redesign.
- Conducting A/B testing by sending traffic to variant pages temporarily.
- Running time-limited promotional campaigns or events.
- Testing new user flows without impacting established URLs.
SEO Impact of 302 Redirects
To consider the SEO impact, it’s important to differentiate when 302 redirects help and when they may cause issues:
- 302 redirects preserve the original page’s SEO value during temporary changes.
- They prevent premature indexing of temporary or unfinished content.
- Misusing 302s for permanent moves can result in loss of link equity and rankings.
- Search engines typically maintain the original URL in search results, but may adapt depending on redirect duration and signals.
Implementing 302 Redirects: Methods and Platforms
Different environments require different implementation methods. Here are the primary approaches:
Server-Side Methods
These methods require access to server configuration files or panels:
- Apache (.htaccess): Using RewriteRule with the [R=302] flag specifies a temporary redirect.
- NGINX: The return 302 directive followed by the target URL implements a temporary redirect.
- Windows Server (IIS): Redirects can be configured via the HTTP Redirect module or web.config settings for 302 status.
CMS-Based Redirects
Content management systems offer user-friendly options:
- WordPress Plugins: Plugins such as Redirection or Yoast SEO Premium allow users to set 302 redirects through a user-friendly interface.
- Magento and other CMS platforms: Often have built-in or extended support for managing temporary redirects.
No-Code Solutions
For quick and temporary redirect needs without server or CMS access:
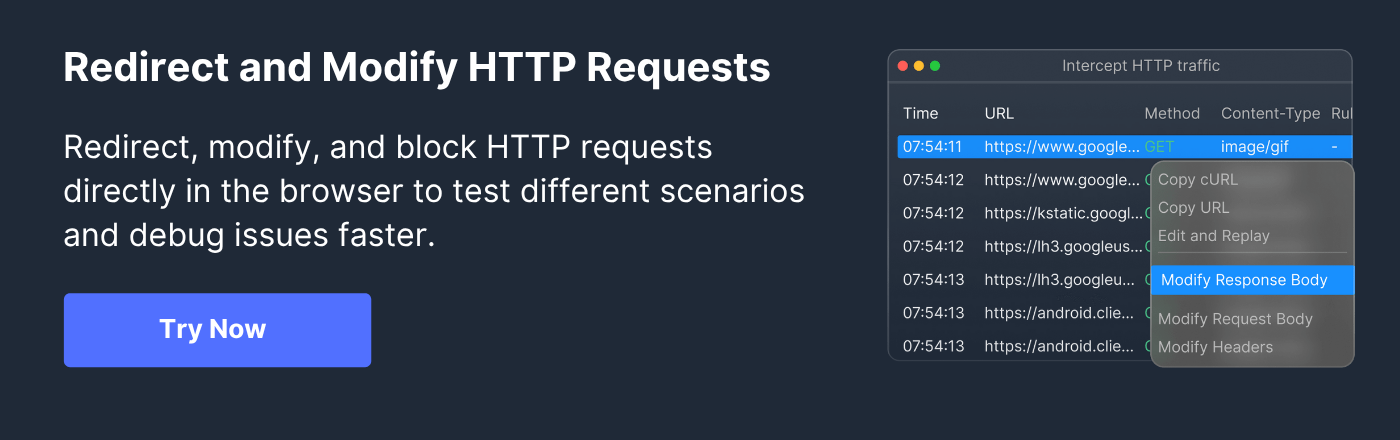
- Requestly HTTP Interceptor: A browser-based tool that lets users create temporary URL redirects instantly, ideal for testing scenarios or rapid redirection without backend changes.
Tools for Managing 302 Redirects
Managing 302 redirects efficiently requires the right tools. These fall into several categories:
- Browser Extensions and Automation Tools: Tools like Requestly HTTP Interceptor help monitor and manage redirects directly in the browser environment.
- WordPress Plugins and CMS Tools: Common plugins provide dashboards for adding, tracking, and editing 302 redirects without manual configuration.
- Server Configuration Utilities: Tools and editors for .htaccess or NGINX configuration files assist in managing redirects at the server level.
- Hosting Control Panels: Control panels like cPanel and Plesk include built-in redirect management features simplifying temporary redirect setup.
Best Practices for Managing Temporary Redirects
To maintain an effective redirect strategy, consider these guidelines:
- Use 302 redirects exclusively for truly temporary changes.
- Document temporary redirects and set clear expiration timelines.
- Avoid creating redirect chains that slow down page loading and dilute SEO.
- Monitor redirects constantly through analytics and audit tools.
- Ensure cross-browser and device compatibility.
- Remove or update redirects promptly after their temporary purpose ends.
Troubleshooting 302 Redirect Issues
If issues arise with 302 redirects, the following approaches help diagnose and resolve common problems:
- Review server files and configurations for conflicting or erroneous rules.
- Check for plugin conflicts within CMS platforms.
- Use browser developer tools and redirect checkers to trace redirect flows.
- Test redirects across multiple browsers and devices to confirm behavior.
Monitoring and Maintenance Strategies
Ongoing monitoring is crucial for healthy website performance. Recommended strategies include:
- Utilize Google Search Console for redirect reports and error detection.
- Analyze page speed and redirect chains using SEO tools.
- Conduct regular audits and reviews after website updates.
- Automate alerts for redirect failures or unusual patterns using monitoring solutions.
Conclusion
302 Temporary Redirects provide an essential mechanism for managing temporary URL changes without affecting long-term SEO. They enable seamless user experiences during site maintenance, testing, or campaigns.
Implementing these redirects through server configurations, CMS tools, or no-code browser solutions like Requestly ensures flexibility and control. Adhering to best practices and regularly monitoring these redirects preserves SEO value and site usability, ensuring that temporary redirects remain timely and effective.

Contents
- What Is a 302 Temporary Redirect?
- How 302 Redirects Work
- Key Differences: 302 vs. 301 Redirects
- Common Use Cases for 302 Redirects
- SEO Impact of 302 Redirects
- Implementing 302 Redirects: Methods and Platforms
- Tools for Managing 302 Redirects
- Best Practices for Managing Temporary Redirects
- Troubleshooting 302 Redirect Issues
- Monitoring and Maintenance Strategies
- Conclusion
Subscribe for latest updates
Share this article
Related posts
Get started today
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!