API Integration Example: Step-by-Step Guide for Developers


Your lightweight Client for API debugging
No Login Required
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!










API integration is the foundation of modern software ecosystems, enabling different applications to communicate and share data seamlessly. Mastering API integration allows developers to build scalable, efficient, and feature-rich applications by enabling diverse systems to work together as one unified platform.
This article explores the technical depth of API integration, covering its definition, benefits, core concepts, real-world examples, integration process, best practices, popular tools, testing methods—including a detailed look at the Requestly API Client—common challenges, and security considerations.
What is API Integration?
API integration is the process of connecting two or more distinct software systems through their Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to enable automatic data exchange and functional interoperability. APIs work as intermediaries that expose specific functionalities or datasets, allowing external applications to consume these resources in a controlled and programmable way.
The key components of API integration include:
- Client: The application initiating the API requests, such as a web client, mobile app, or server-side component.
- Server/API Provider: The system providing endpoints that expose data or services.
- Middleware (optional): An intermediary service that orchestrates, transforms, or manages API traffic, especially in complex systems.
This integration enables automation, modular architecture, and real-time or asynchronous communication between software components, which is essential for microservices, SaaS platforms, IoT, and cloud applications.
Benefits of API Integration
Integrating APIs offers significant operational and strategic advantages:
- Operational Efficiency: Automates tasks that would otherwise require manual data transfers, drastically reducing human error and processing times.
- Extended Functionality: Taps into external services such as payment processors, messaging platforms, geolocation services, and analytics, avoiding redundant development.
- Seamless User Experiences: Enables consistent and up-to-date information sharing across platforms, devices, and services, improving overall user satisfaction.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Eases the addition or replacement of services without rewriting core business logic.
- Faster Development Cycles: Accelerates product launches by leveraging pre-built APIs that fulfill specialized needs.
- Cost Reduction: Lowers maintenance costs by outsourcing complex functionalities to specialized providers.
These benefits collectively enable businesses to stay competitive, responsive, and adaptable.
Key Concepts in API Integration
Successful API integration depends on a thorough understanding of essential technical concepts:
- Endpoints: Specific URLs representing resources or functions that the API exposes, such as /users or /transactions.
- HTTP Methods: Define the type of operation—GET (read), POST (create), PUT/PATCH (update), DELETE (remove)—that can be performed on endpoints.
- Authentication & Authorization: Secures access using mechanisms such as API keys, OAuth 2.0, JWT tokens, or mutual TLS, ensuring only permitted clients can utilize the API.
- Request and Response Formats: Typically JSON or XML structured data describing the inputs and outputs of API operations.
- Rate Limiting: Throttling mechanisms imposed by APIs to restrict the number of requests in a given time window to protect backend resources.
- Error Handling: Standardized methods to report and resolve issues, usually indicated by HTTP status codes and descriptive error messages.
- Versioning: Managing API changes by maintaining multiple versions to avoid breaking existing integrations.
Mastering these concepts ensures scalable, maintainable, and secure API integrations.
Common API Integration Examples and Use Cases
Numerous industries capitalize on API integrations to enhance their products and services. Some detailed examples include:
- Payment Integration: Utilizing Stripe or PayPal APIs to securely handle transactions, refunds, and subscriptions within applications.
- Social Login and Sharing: Integrating with Facebook, Google, or Twitter APIs for user authentication or content sharing, eliminating redundant credential management.
- Geolocation Services: Embedding interactive maps and location-based functionalities through Google Maps or Mapbox APIs, including real-time routing and place searches.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Synchronizing contact details and sales activities with Salesforce or HubSpot APIs for unified sales and marketing workflows.
- Communication Platforms: Sending SMS, emails, or voice calls programmatically using Twilio API, enabling personalized customer interactions.
- E-commerce Automation: Syncing inventory, orders, and shipping details via Shopify or WooCommerce APIs to streamline supply chain logistics.
- Analytics and Reporting: Pulling usage data and trends from Google Analytics API or other BI tools for actionable insights.
These use cases demonstrate how API integration enables business innovation and operational excellence.
Step-by-Step API Integration Process
Integrating an API is a multi-stage technical process that requires careful attention and adherence to best practices:
- Review API Documentation Thoroughly: Understand all aspects of the API, including base URLs, endpoints, supported methods, required parameters, authentication, rate limits, and data formats. Good documentation reduces guesswork and helps scope integration complexity.
- Setup Authentication and Authorization: Depending on the API’s security model, obtain credentials such as API keys, client ID/secret pairs, or tokens. Implement token generation and renewal protocols, especially for OAuth flows where user consent may be involved.
- Build Communication Client: Use HTTP client libraries (e.g., Axios, HttpClient, Requests) for synchronous or asynchronous calls. Properly configure request headers, timeouts, and error handling mechanisms.
- Data Parsing and Transformation: Convert input and output data to match your internal data models. Handle different date formats, nested objects, or complex arrays carefully to maintain integrity.
- Handle Pagination and Rate Limits: Integrate logic for paginated responses using tokens or offsets and respect API rate limits by implementing throttling or backoff algorithms.
- Implement Error Handling and Logging: Detect and classify errors based on HTTP status codes and error bodies. Use logging frameworks to record request-response cycles, enabling easier debugging and auditing.
- Test Integration Thoroughly: Perform unit tests, integration tests, and system tests to verify data correctness, exceptional cases, and performance under load.
- Deploy and Monitor: Deploy the integration in a controlled environment, monitor API usage, latency, and failure rates continuously. Use analytics and alerting tools to preempt potential issues.
Best Practices for Building API Integrations
To maintain robustness and scalability, apply these best practices:
- Strict Adherence to Documentation and Standards: Avoid undocumented or unsupported API features. Use JSON Schema or OpenAPI specifications to validate requests and responses.
- Security-First Approach: Use HTTPS exclusively, protect secrets, avoid logging sensitive data, and use scopes or roles to limit privilege levels.
- Graceful Degradation and Retry Logic: Build fallbacks for degraded service or intermittent issues. Implement retries with exponential backoff to handle transient network problems.
- Version Awareness: Always specify targeted API versions explicitly in URLs or headers to avoid unexpected breakage when APIs evolve.
- Modular and Reusable Integration Code: Encapsulate API communication in dedicated modules or services, enabling easier updates and testing.
- Comprehensive Monitoring and Alerts: Track API response times, errors, and usage patterns with proper instrumentation.
Following these practices will ensure your API integrations remain maintainable and secure over time.
Popular Tools for API Integration Development
An effective API integration process is supported by a comprehensive set of development and testing tools that streamline design, documentation, execution, security, and debugging:
- API Design and Documentation: Postman, Swagger (OpenAPI), and Stoplight simplify the creation, documentation, and sharing of APIs. These tools facilitate collaboration by providing clear specifications and interactive API documentation.
- HTTP Client Libraries: Libraries like Axios (JavaScript), Python Requests, and Java HttpClient simplify making HTTP requests programmatically by handling connection logic, headers, and asynchronous operations.
- API Management Platforms: Solutions such as Kong, Apigee, and Azure API Management provide enterprise-grade features including security enforcement, rate limiting, analytics, versioning, and lifecycle management.
- Automation Frameworks: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and other CI/CD tools automate API testing and deployment, ensuring integrations are continuously validated throughout development cycles.
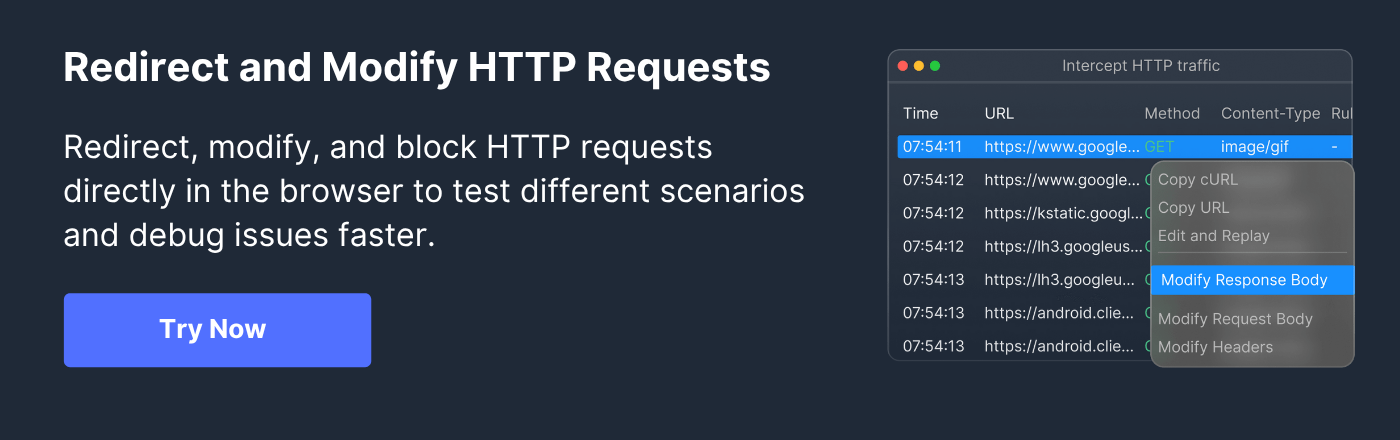
- Debugging Proxies and Interceptors: Traditional tools like Fiddler and Charles Proxy enable inspection, interception, and modification of HTTP traffic, crucial for diagnosing issues.
- Requestly API Client: A modern, browser-integrated API client and HTTP interceptor that combines the capabilities of an API testing tool with seamless real-time request and response interception and modification. It supports:
- Organizing API requests into collections and managing multiple environments for streamlined workflows.
- Editing request headers, query parameters, and payloads on the fly without backend changes.
- Mocking API responses to simulate backend behavior during frontend development or testing.
- Supporting multiple authentication schemes including API keys, OAuth 2.0, and Bearer tokens.
- Automating workflows with pre-request and post-response JavaScript scripting.
- Collaborating via shared workspaces and history replay for debugging and regression testing.
- Operating directly within the browser or via a desktop app, eliminating VPN or proxy setup issues.
- Importing Postman collections for easy migration.
Requestly empowers developers and QA teams by offering a unified, intuitive platform that accelerates API integration, debugging, and testing workflows, making it invaluable in complex, multi-environment API ecosystems.
These tools help streamline development, testing, and maintenance phases.
Testing API Integration: Methods and Tools
Testing is crucial to ensuring your integrations work accurately and reliably under all expected conditions. Testing occurs at various stages:
- Unit Testing checks individual API calls for expected response under simulated conditions.
- Integration Testing validates complete workflows involving multiple API calls.
- Load Testing assesses performance and stability under heavy traffic.
One tool that significantly enhances API integration testing is the Requestly API Client. It offers:
- Real-time interception and editing of HTTP requests and responses within browser sessions.
- Header manipulation, URL redirection, and response mocking without changing backend code.
- Collaborative features suitable for development and QA teams.
- A lightweight, browser-based alternative to complex proxies.
Requestly empowers developers to debug API behaviors immediately, test different scenarios effortlessly, and accelerate issue resolution in integration workflows.
Troubleshooting Common API Integration Issues
Integrations can fail or produce unexpected results due to various reasons:
- Authentication or Authorization Failures: Incorrect or expired tokens, missing scopes.
- Incorrect Request Parameters: Missing or malformed fields causing validation errors.
- Data Format Mismatches: Fields expected as strings but sent as numbers, or JSON keys not aligning.
- Rate Limit Exceeding: APIs rejecting requests after quota exhaustion.
- Network or Connectivity Issues: Timeouts, DNS failures, or SSL errors.
- Versioning Changes: Backward incompatible API upgrades breaking clients.
Effective troubleshooting strategies include detailed log analysis, capturing full request-response cycles, using debugging tools like Requestly to replay requests or simulate server responses, and testing edge cases systematically.
Security Considerations in API Integration
Security is paramount in API integrations, as improper controls expose data and systems to attacks. Key considerations are:
- Use HTTPS to encrypt data in transit.
- Implement strong authentication such as OAuth 2.0 or mutual TLS.
- Validate and sanitize all inputs and outputs to prevent injection attacks.
- Limit API permissions to the least required scopes.
- Protect API keys and secrets, never expose them in client-side code.
- Monitor access patterns and use anomaly detection to flag suspicious behavior.
- Use logging and auditing to maintain traceability of API usage.
Following security best practices shields your integrations from common vulnerabilities and compliance risks.
Summary
API integration is an intricate yet indispensable aspect of software development, facilitating seamless interaction between diverse systems.
By comprehensively understanding integration processes, adhering to best practices, leveraging modern tools like Requestly API Client for testing and debugging, and maintaining a vigilant security posture, developers can build robust, scalable, and secure integrations. As software ecosystems continue to expand and interconnect, mastering API integration is essential for delivering efficient and innovative digital solutions.

Contents
- What is API Integration?
- Benefits of API Integration
- Key Concepts in API Integration
- Common API Integration Examples and Use Cases
- Step-by-Step API Integration Process
- Best Practices for Building API Integrations
- Popular Tools for API Integration Development
- Testing API Integration: Methods and Tools
- Troubleshooting Common API Integration Issues
- Security Considerations in API Integration
- Summary
Subscribe for latest updates
Share this article
Related posts
Get started today
Requestly is a web proxy that requires a desktop and desktop browser.
Enter your email below to receive the download link. Give it a try next time you’re on your PC!